[ad_1]
If Leo Tolstoy had been writing about right now’s enterprise situations, he might need famous that comfortable economies are all alike however each sad economic system is sad in its personal method.
China’s development prospects have been hammered by strict Covid-19 lockdowns in a bid to quell its Omicron outbreak; the US Federal Reserve dangers turning an American increase into bust; Europe’s households are enduring a value of dwelling disaster; and the scenario is worse in lots of poorer rising markets, the place meals crises and even famines beckon.
These 4 totally different however imposing issues every stalk the worldwide economic system because it recovers from the pandemic and it’s not shocking the temper is darkening.
In line with Robin Brooks, chief economist of the Institute of Worldwide Finance, the confluence of those shocks suggests the world economic system is already in bother. “We’re in one other international recession scare now, besides this time we expect it’s for actual,” he says.

Monetary markets have taken fright. The MSCI world index of equities fell greater than 1.5 per cent up to now week, greater than 5 per cent in Could and greater than 18 per cent since a peak in early January. Dhaval Joshi, chief strategist at BCA Analysis, notes that on prime of a torrid time for shares, there was a sell-off in bonds, inflation-protected bonds, industrial metals, gold and crypto property.
“The final time that the ‘every thing sell-off’ star alignment occurred was in early 1981 when Paul Volcker’s Fed broke the again of inflation and turned stagflation into an outright recession,” Joshi says.
Defining a world recession is not any straightforward job. For particular person nations, some economists outline a “technical recession” as two consecutive quarters of contraction in gross home product. The Monetary Occasions prefers a extra versatile definition as does the US, the place the Nationwide Bureau of Financial Analysis defines a recession as “a major decline in financial exercise that’s unfold throughout the economic system and that lasts quite a lot of months”.
At a world scale definitions change into nonetheless tougher. The IMF and World Financial institution favor to characterise a world recession as a 12 months during which the typical international citizen experiences a drop in actual revenue. They spotlight 1975, 1982, 1991, 2009 and 2020 because the dates of the earlier 5 international recessions.
Whereas the official international development forecasts for 2022 nonetheless appear far off this definition — in April the IMF anticipated annual development of three.6 per cent this 12 months — this determine relates as a lot to the restoration within the second half of 2021 as to expectations for 2022. When the fund appears on the development it expects throughout 2022, it has already minimize its forecast from 4.5 per cent in October final 12 months to 2.5 per cent in April.
Brooks reckons that the information since this forecast was printed has been sufficiently dangerous to decrease the expansion projection to simply 0.5 per cent throughout 2022, lower than the anticipated enhance in inhabitants. “Mounting international recession danger is top-of-mind for markets, which has vital repercussions for investor psychology,” Brooks says.
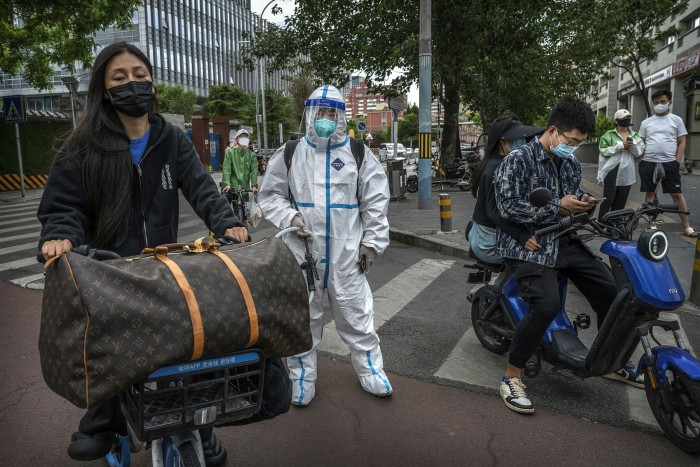
China is the large economic system that almost all economists are anxious about and the previous week has seen new information reinforcing issues about its prospects. Accounting for 19 per cent of the world’s whole output, China is now so massive that when it catches Covid the remainder of the world can not ignore its ache, particularly due to its influence on international provide chains and its demand for items and companies from different nations.

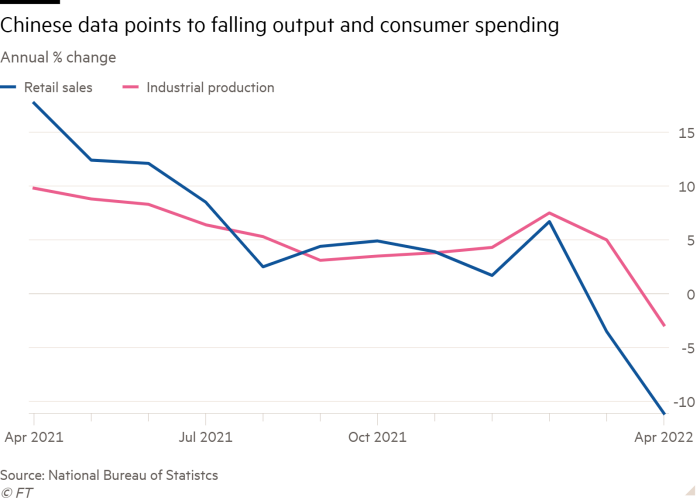
Extreme strains are exhibiting. With lockdowns rippling by the nation, ships queue outdoors Chinese language ports and the nation’s manufacturing and retail sectors have began to contract. Retail gross sales fell 11 per cent 12 months on 12 months in April, whereas industrial manufacturing was down 3 per cent. China’s house gross sales additionally dropped extra final month than in early 2020, when its economic system went into reverse, regardless of the Folks’s Financial institution of China loosening financial coverage to encourage borrowing and spending. Unemployment is rising.
Kevin Xie, senior Asia economist on the Commonwealth Financial institution of Australia, says that China’s financial information in April was constantly disappointing. Though the outlook relies upon crucially on the unfold of Covid, he provides, “falling employment and weakened confidence amongst enterprise and households will curb spending and bode poorly for the expansion outlook”.
Within the US, the opposite international financial powerhouse, the economic system is affected by the pandemic’s legacy and, particularly, extreme fiscal stimulus that arguably ran the economic system too sizzling and generated excessive inflation even with modest vitality value rises. Alongside a really tight labour market, the Fed has been compelled to concede an error and has now moved decisively right into a part of tightening financial coverage to sluggish development and produce inflation down.

The Fed chair Jay Powell was crystal clear this week that the central financial institution would proceed elevating rates of interest till it noticed “clear and convincing” proof that inflation was returning to the two per cent goal. He was not involved about unemployment rising “a couple of ticks” from the present low stage of three.6 per cent.
Powell added that he was aiming at a mushy touchdown for the economic system, however many in monetary markets suppose that is perhaps onerous to attain. Krishna Guha, vice-chair of Evercore ISI, warns there’s a a lot increased than regular danger that the powerful discuss from officers, economists and market contributors would change into a self-fulfilling prophecy and generate a downturn.
“To say a softish touchdown is feasible is to not say it’s inevitable and even significantly seemingly,” Guha says. Though he’s not predicting a US recession, Guha says, “bringing inflation below management with no recession and huge enhance in unemployment . . . might be difficult”.
On the opposite facet of the Atlantic, Europe’s equally tough downside is totally different. Other than the UK, inflation stems nearly universally from increased vitality costs fairly than an overheating economic system and may be traced on to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.

Sadly for the EU, understanding the reason for Europe’s woes doesn’t diminish its penalties. With inflation of seven.4 per cent in April, eurozone costs are rising a lot sooner than its citizen’s incomes, imparting successful to dwelling requirements that may restrict spending and the restoration from the pandemic. New forecasts from the European Fee this week had been scaled again sharply and implied stagnation within the second quarter of 2022.
The fee expects the economic system to recover from this tough interval and return to cheap development of about half a per cent per quarter by the summer time, however many non-public sector economists suppose the hit to incomes can have longer-lasting results. Christian Schulz, an economist at Citi, says that the official forecasts seem too optimistic and it’s extra seemingly there might be “nearly no development for the remainder of the 12 months”.
If Europe’s issue is in adjusting to a lot increased vitality costs, poorer nations have the even more durable job of coping with the fast rise within the value of meals, which account for greater than 30 per cent of expenditure in rising economies.
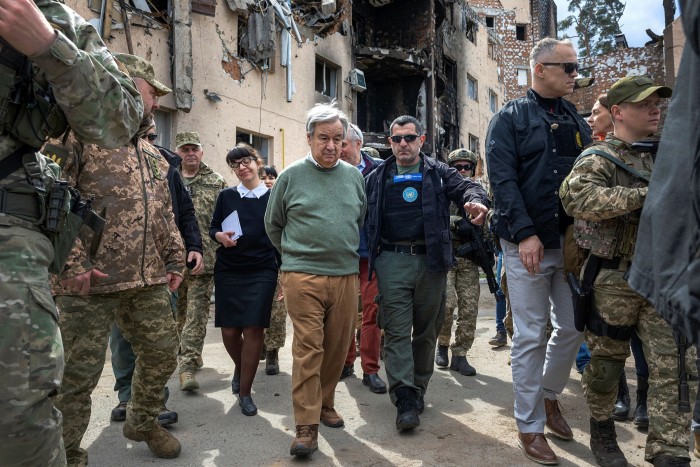

With the Black Sea ports that Ukraine makes use of for exporting grains shut, fears of a meals disaster later this 12 months are mounting. António Guterres, secretary-general of the UN, stated on Wednesday that the battle in Ukraine, approaching prime of present pressures on meals costs, “threatens to tip tens of hundreds of thousands of individuals over the sting into meals insecurity adopted by malnutrition, mass starvation and famine”.
Though it has its personal home political and financial crises, Sri Lanka epitomises the dire decisions confronted in lots of the world’s poorest nations when it determined this week to default on its international debt for the primary time. This, it stated, was essential to make use of its onerous forex for importing gasoline, meals and medication.
India, in the meantime, intensified the issues in different rising economies by reneging on a pledge to not ban the export of grain this week. Wheat costs rose once more and are up greater than 60 per cent this 12 months.

Naturally, as recession dangers rise, one of the best information for the worldwide economic system can be a Russian withdrawal from Ukraine and an finish to the zero-Covid technique in China. This isn’t within the reward of financial ministers and officers, so as an alternative, they’ll once more must effective tune their response to the tough conditions they face.
In Europe and rising economies, this may contain assuaging the implications of upper meals and vitality costs — elevating advantages and subsidising meals and vitality in nations with sufficiently sturdy public funds. The US and UK might speed up the tightening cycle of financial coverage, whereas China will search to restrict the unfavourable results of the Omicron coronavirus wave in China.
The bulk view amongst economists is that the defence towards international recession will nonetheless win in 2022. However economists are more and more hedging their bets within the face of relentless dangerous information.
Innes McFee, chief international economist at Oxford Economics, says there may be little query that the worldwide financial enlargement is near a peak, that it’s slowing and that policymakers might want to work out how a lot tightening is required. However, he says, a recession continues to be unlikely for now as a result of policymakers nonetheless have the instruments to again away and stimulate if issues worsen.
“Recession dangers rise into subsequent 12 months, however they don’t seem to be that prime presently,” McFee says.
[ad_2]
Source_link



